
It’s important to know the difference between aplastic crisis and aplastic anemia. At Liv Hospital, we focus on clear diagnoses and effective treatments. An aplastic crisis is when red blood cell production suddenly stops. It’s often caused by parvovirus B19 in people with certain blood disorders.
Aplastic anemia, on the other hand, is a long-term problem where the bone marrow fails to make blood cells. We aim to give top-notch healthcare and support to international patients. This helps them deal with these complex conditions.
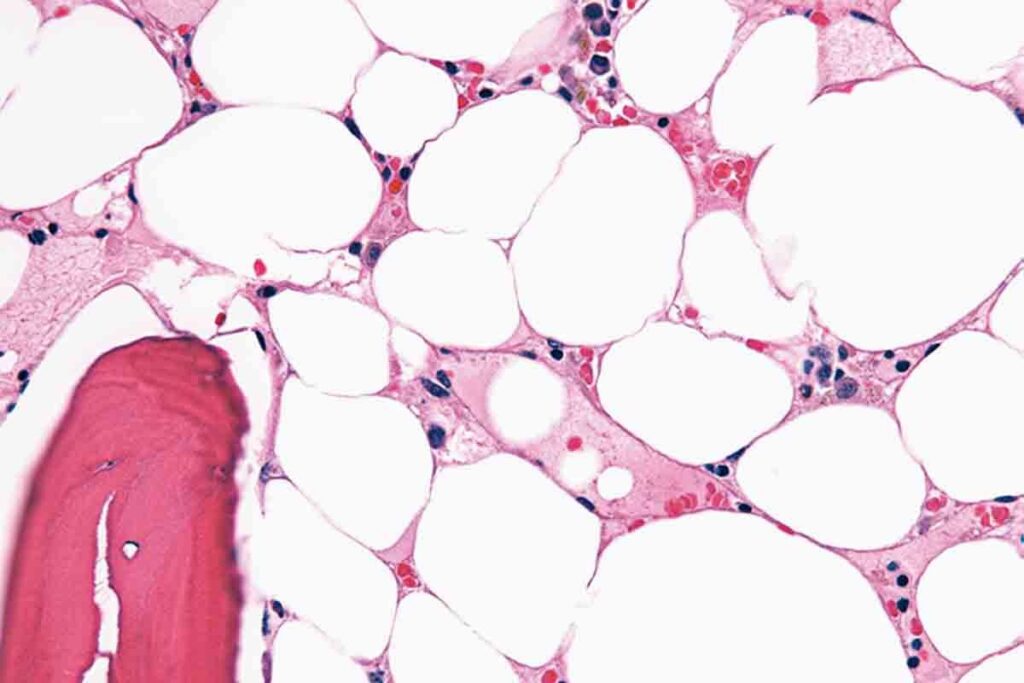
It’s important to know how blood cells are made to understand blood disorders like aplastic crisis and anemia. Blood cells are produced in the bone marrow through a complex process called hematopoiesis.
Hematopoiesis is how our body makes blood cells, including red and white blood cells, and platelets. It starts with stem cells that can turn into any blood cell type. Growth factors and cytokines control this process to make the right blood cells at the right time.
The bone marrow is key to making blood cells in adults. It’s the spongy tissue in bones like the hips and thighbones. It has stem cells that grow into different blood cells. The health of the bone marrow is vital for blood cell production, and damage can cause problems like aplastic anemia.
Controlling blood cell production is complex, with many feedback loops. The body checks blood cell levels and adjusts production. For example, if red blood cells drop, the kidneys make more erythropoietin. This hormone tells the bone marrow to make more red blood cells. Knowing this helps us understand conditions like pancytopenia, where all blood cell types are low.

An aplastic crisis is a serious condition where the bone marrow fails. It mainly affects people with certain blood disorders. This failure leads to a sharp drop in red blood cells, making anemia much worse.
An aplastic crisis is when the bone marrow stops making red blood cells. It’s often caused by infections, like parvovirus B19, in people with chronic blood diseases. Symptoms include a quick drop in hemoglobin, low reticulocyte count, and severe anemia.
Unlike some other bone marrow failures, an aplastic crisis is temporary. With the right care, the bone marrow can start making red blood cells again. This makes it different from long-lasting bone marrow disorders.
The main cause of an aplastic crisis is parvovirus B19 infection. This virus attacks red blood cell precursors in the bone marrow, stopping their production. People with blood disorders are more at risk because their red blood cells don’t last long.
Other factors that can harm bone marrow include toxins or drugs. But parvovirus B19 is the biggest risk factor.
Aplastic anemia affects how bone marrow makes blood cells. It’s a serious condition where the bone marrow can’t produce enough blood cells. This leads to pancytopenia.
Aplastic anemia means the bone marrow can’t make blood cells. This includes red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. It causes pancytopenia, a drop in these blood cells.
The problem is caused by the immune system attacking the bone marrow. This stops it from making blood cells.
Key aspects of aplastic anemia include:
Aplastic anemia is a long-term condition. It needs ongoing care and treatment. Unlike aplastic crisis, which is short-term, aplastic anemia lasts a long time.
“Aplastic anemia is a chronic and life-threatening condition that requires prompt and effective treatment to manage its symptoms and prevent complications.”
Aplastic anemia is divided into different levels based on its severity. This is based on how low the blood cell counts are and the patient’s health. The level helps doctors decide how to treat it and what to expect.
| Severity | Blood Cell Counts | Clinical Implications |
| Severe | Low counts of two or more cell lines | High risk of infections and bleeding |
| Moderate | Reduced counts, not meeting severe criteria | Variable risk requires monitoring |
Knowing the level and severity of aplastic anemia is key. It helps doctors choose the right treatment and manage the condition well.
Aplastic crisis and aplastic anemia are related but different. They have different causes, lengths, and outcomes. Knowing these differences helps in making the right diagnosis and treatment.
Aplastic crisis often comes from a virus like parvovirus B19. It stops the body from making red blood cells. Aplastic anemia, on the other hand, is caused by the immune system attacking bone marrow cells. It can also be due to toxins or genetics.
The causes of these conditions are quite different. Aplastic crisis is a short-term stop in red blood cell production. Aplastic anemia is a long-term problem where the bone marrow can’t make blood cells well.
Aplastic crisis is short-lived, usually getting better once the cause is gone. Aplastic anemia, though, is a long-term issue that needs ongoing care.
Aplastic crisis mainly affects red blood cells. Aplastic anemia affects many cell types, leading to a lack of all blood cells.
The impact on different blood cells is a key difference. Here’s a table showing the main differences:
| Condition | Affected Cell Lines |
| Aplastic Crisis | Primarily red blood cells |
| Aplastic Anemia | Multiple cell lines (red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets) |
The outcomes and chances of recovery differ. Aplastic crisis usually has a good outlook with the right care. Aplastic anemia needs more treatment and has a less certain outcome.
Doctors need to understand these differences. This helps them give the best care. It also helps patients know what to expect from their treatment.
Understanding aplastic crisis and aplastic anemia is key to the right diagnosis and treatment. Both affect blood cell production but show different symptoms.
Aplastic crisis causes a sudden drop in red blood cells, often from infections like parvovirus B19. Symptoms include:
This condition can be life-threatening if not treated quickly. Seek immediate medical care to manage it and avoid complications.
Aplastic anemia is a long-term condition where the bone marrow doesn’t make enough blood cells. Symptoms can vary and include:
A medical expert notes, “Aplastic anemia can have many symptoms due to pancytopenia. It’s vital to diagnose and treat it quickly.” The severity of symptoms depends on how much the bone marrow fails.
Both conditions can have symptoms like fatigue and weakness from anemia. But aplastic anemia often has more symptoms because of pancytopenia.
| Symptom | Aplastic Crisis | Aplastic Anemia |
| Severe Anemia | Common | Variable |
| Increased Infections | Less Common | Common |
| Bleeding/Bruising | Less Common | Common |
Seek medical help if you have severe fatigue, frequent infections, or unexplained bleeding. Early treatment can greatly improve outcomes for both conditions.
If symptoms worsen or you have severe symptoms, get medical help right away. Your doctor can guide you on the best treatment.
Diagnosing aplastic crisis and aplastic anemia requires a detailed strategy. This includes lab tests, bone marrow exams, and sometimes viral studies. Getting the diagnosis right is key to choosing the right treatment and improving patient care.
Laboratory tests are essential in diagnosing aplastic crisis and aplastic anemia. A complete blood count (CBC) is usually the first step. It shows the levels of different blood cells, like red and white blood cells, and platelets.
Key laboratory findings may include:
| Laboratory Test | Normal Range | Aplastic Crisis/Anemia Findings |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.5-17.5 | Decreased |
| White Blood Cell Count (cells/μL) | 4,500-11,000 | Decreased |
| Platelet Count (cells/μL) | 150,000-450,000 | Decreased |
A bone marrow examination is a key diagnostic tool. It involves taking a sample of bone marrow for microscopic examination.
Bone marrow findings in aplastic anemia may include:
In some cases, viral studies and genetic testing are needed. This helps find underlying causes or contributing factors. For example, tests for hepatitis or HIV may be done.
Genetic testing can also identify inherited conditions that may lead to aplastic anemia.
Differential diagnosis is about ruling out other conditions with similar symptoms or lab findings. This includes myelodysplastic syndromes or leukemia.
A detailed diagnostic evaluation is vital. It helps distinguish between aplastic crisis and aplastic anemia. It also identifies any underlying conditions that need specific treatment.
It’s key to know about pancytopenia to tackle aplastic anemia and other blood issues. Pancytopenia means fewer red, white blood cells, and platelets. It’s a big sign of aplastic anemia, a serious bone marrow failure.
Pancytopenia means fewer red, white, and platelet cells. This can cause anemia, infections, and bleeding problems. Doctors check blood counts and bone marrow to find the cause.
Aplastic anemia often causes pancytopenia. When the bone marrow can’t make enough blood cells, pancytopenia happens. Knowing this link helps doctors plan better treatments.
Key features of aplastic anemia that lead to pancytopenia include:
Pancytopenia is common in aplastic anemia, but it can also be caused by other things. To tell if it’s aplastic anemia, doctors do tests like bone marrow biopsies and genetic tests.
Pancytopenia is a critical condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. Understanding its causes and relation to aplastic anemia is essential for effective management.”
Pancytopenia can also come from other issues, like:
Finding out why someone has pancytopenia is important for the right treatment. Doctors need to do detailed tests to figure out the cause and plan the best care.
‘Bone marrow anemia’ is a term for conditions where the bone marrow can’t make enough blood cells. This is linked to other bone marrow failure syndromes.
Bone marrow anemia happens when the bone marrow can’t make enough red or white blood cells or platelets. This can cause fatigue, infections, and bleeding problems.
Bone marrow failure syndromes include aplastic anemia and myelodysplastic syndromes. These are when the bone marrow can’t make blood cells.
Aplastic anemia is a specific bone marrow failure syndrome. It’s a chronic condition where the bone marrow can’t make blood cells. It needs careful management to avoid serious health issues.
Bone marrow anemia is different from other anemias. It’s caused by the bone marrow’s failure to produce blood cells. Key signs include:
Managing aplastic crisis and aplastic anemia needs a deep understanding of their treatments. We will cover the best ways to handle these conditions. This includes the latest and most effective treatments.
Handling aplastic crisis means supportive care and finding the cause. The main goal is to help the body make blood cells again until it gets better.
Treating aplastic anemia is more complex. It involves immunosuppressive therapy and bone marrow transplantation in some cases. The treatment choice depends on how severe the condition is and the patient’s health.
Immunosuppressive therapy tries to stop the immune system from attacking the bone marrow. This lets the bone marrow recover. This method is used for patients who can’t have bone marrow transplantation.
Bone marrow transplantation, or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, is a possible cure for aplastic anemia. It replaces damaged bone marrow with healthy stem cells from a donor.
The treatment plan for aplastic anemia should be made just for the patient. It takes into account age, health, and how severe the condition is.
The outlook for patients with aplastic crisis and anemia depends on several factors. These include how severe the condition is and how well it responds to treatment. Knowing these factors helps manage expectations and make informed care decisions.
Recovery from aplastic crisis is often good if the cause is found and treated quickly. The bone marrow usually starts working again once the problem is fixed. For example, if a virus caused it, getting better happens after the virus goes away.
Key factors influencing recovery include:
The long-term outlook for aplastic anemia varies. It depends on how severe the disease is and how well it responds to treatment. Those with severe anemia who get the right treatment, like immunosuppressive therapy or bone marrow transplant, can live longer and have a better life.
| Disease Severity | Treatment Response | Long-term Outlook |
| Severe | Positive | Favorable, with long-term survival possible |
| Moderate | Variable | Guarded, ongoing management needed |
| Mild | Generally positive | Generally good, with regular monitoring |
Many factors can affect outcomes for aplastic anemia patients. These include how severe the disease is at diagnosis, the patient’s age, and how well they respond to treatment. Other health issues can also make things harder and affect the prognosis.
Patients need to work closely with their healthcare team to monitor their condition and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
Quality of life is very important for patients with aplastic anemia. While treatment can be tough, many patients can live active lives with the right care. Supportive care, like transfusions and preventing infections, helps a lot in keeping the quality of life good.
Understanding the prognosis and long-term outlook helps patients and their families deal with the challenges of aplastic crisis and anemia.
It’s key to know the difference between aplastic crisis and aplastic anemia for the right treatment. We’ve looked at how they are different in this article. This includes their causes, symptoms, and how to treat them.
Aplastic crisis and aplastic anemia have different causes and effects. Aplastic crisis is short-term and often caused by viruses. On the other hand, aplastic anemia is a long-term problem with the bone marrow. Knowing these differences helps doctors treat patients better.
Diagnosing aplastic crisis versus aplastic anemia involves many steps. Doctors use lab tests, bone marrow exams, and look at how the patient feels. This helps them understand and treat the condition properly.
In summary, getting the right diagnosis and treatment is vital for aplastic crisis and aplastic anemia. This approach can greatly improve the lives of those with these conditions.
Aplastic crisis is a short-term issue often caused by parvovirus B19. It mainly affects red blood cells. On the other hand, aplastic anemia is a long-term problem where the bone marrow fails to make blood cells. This leads to a lack of all blood cell types.
Aplastic anemia is a long-term condition where the bone marrow can’t make blood cells. This results in pancytopenia, a condition with fewer red and white blood cells and platelets.
Doctors use lab tests to diagnose aplastic crisis. These tests include complete blood counts to check for anemia. They might also look for parvovirus B19 infection.
Treatment for aplastic anemia includes medicines to suppress the immune system. In some cases, a bone marrow transplant is considered. The choice depends on how severe the condition is and the patient’s health.
Aplastic crisis and aplastic anemia are different conditions. But severe or repeated aplastic crises might slightly increase the risk of other bone marrow failure syndromes. It’s not a direct cause of aplastic anemia.
Most people recover from aplastic crisis well. Once the cause, like parvovirus B19, is gone, the bone marrow usually starts working again.
The severity of aplastic anemia greatly affects the outlook. More severe cases have a worse prognosis. How well the patient responds to treatment also plays a big role in the long-term outlook.
Bone marrow anemia is when the bone marrow can’t make enough red blood cells. Aplastic anemia is a specific type of bone marrow failure. It affects the production of all blood cell types, not just red blood cells.
Yes, patients with aplastic anemia face ongoing management challenges. They may deal with treatment side effects, increased infection risk, and the emotional impact of a chronic condition.
Pancytopenia is a feature of aplastic anemia, but it can also be caused by other things. To tell if it’s aplastic anemia, doctors do tests like bone marrow exams. These help find the real cause of pancytopenia.
Have questions or need assistance? Our team is here to help you with appointments, services, or general inquiries.