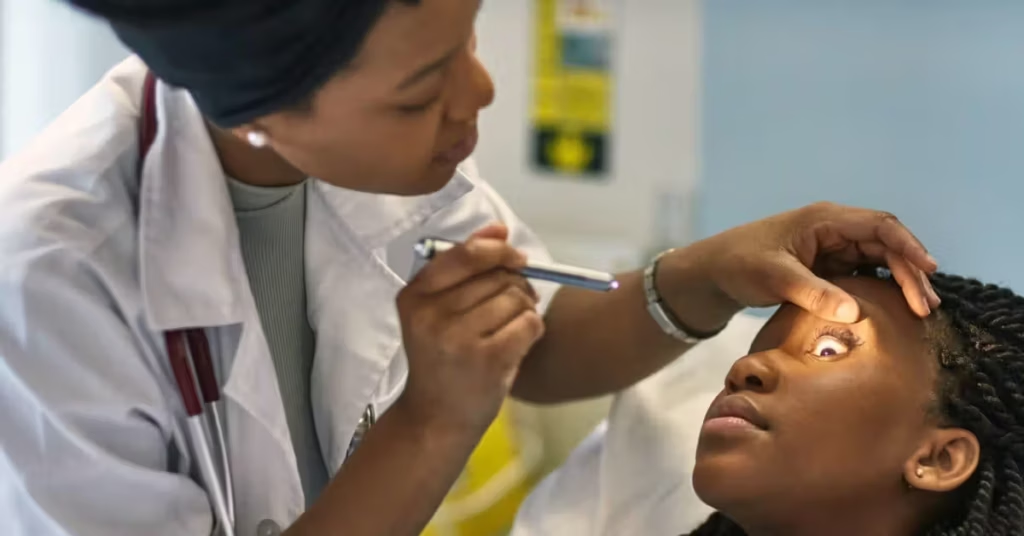
The Excimer Laser is a highly advanced medical technology that produces precise ultraviolet light pulses to perform delicate surgical and therapeutic procedures. By enabling controlled ablation of tissue without excessive thermal damage, this laser system has become a cornerstone in ophthalmology, dermatology, and various medical interventions. Its precision, safety, and adaptability make it a vital tool within modern medical technologies.
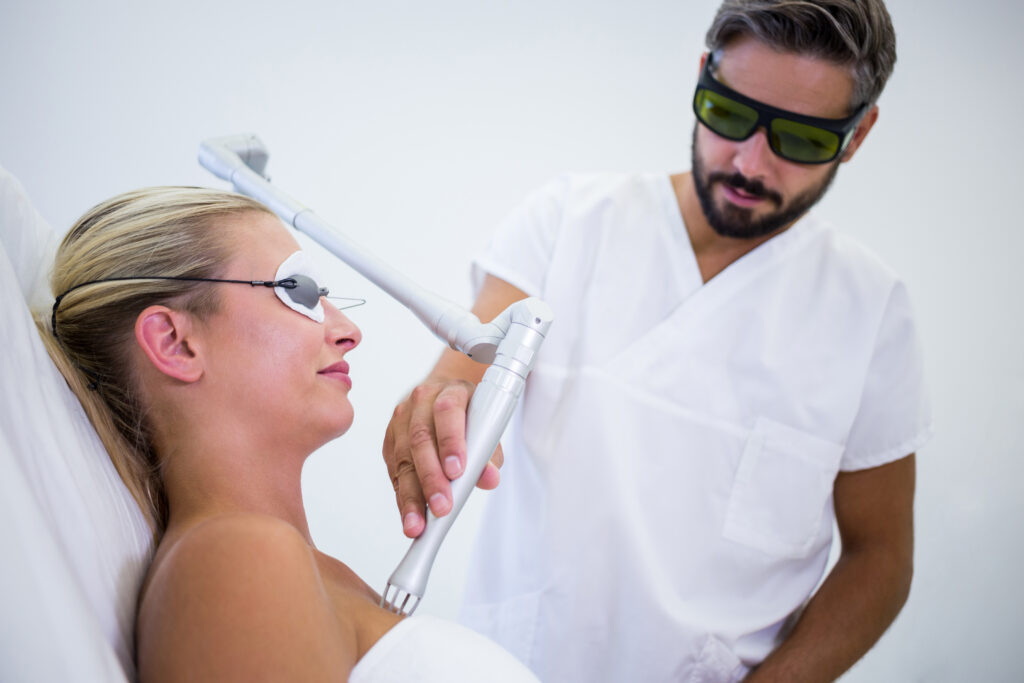

The Evolution of Excimer Laser Technology
Traditional surgical techniques often involved mechanical instruments that could inadvertently damage surrounding tissues. The development of excimer lasers introduced a non-contact, high-precision alternative.
Initially applied in corneal reshaping procedures for vision correction, excimer lasers have expanded into dermatology, cardiology, and research applications. Modern systems combine advanced optics, computer-assisted targeting, and real-time monitoring to achieve highly controlled outcomes, minimizing patient risk.
How Excimer Lasers Work
Excimer lasers emit short ultraviolet light pulses that break molecular bonds in tissue through a process called photoablation. Unlike thermal lasers, excimer lasers remove tissue precisely without significant heat generation, reducing collateral damage.
In ophthalmology, for example, the laser reshapes the cornea to correct refractive errors such as myopia, hyperopia, or astigmatism. The laser system is guided by advanced computer algorithms that customize the treatment according to the patient’s unique corneal topography and visual prescription.
Key Advantages of Excimer Laser Technology
- High Precision and Control
Excimer lasers enable micron-level ablation, allowing specialists to perform delicate procedures with unmatched accuracy. - Minimized Thermal Damage
The ultraviolet laser light removes tissue without significant heating, preserving surrounding structures and reducing recovery time. - Customizable Treatments
Computer-guided systems allow personalized adjustments for each patient’s anatomy and treatment goals. - Wide Range of Applications
Excimer lasers are used in ophthalmology, dermatology, and experimental procedures requiring precise tissue ablation. - Rapid and Efficient Procedures
Short pulse durations and controlled energy delivery enable faster treatments while maintaining safety and precision.
Applications Across Medical Fields
Ophthalmology
Excimer lasers are integral to LASIK, PRK, and other refractive surgeries. They reshape the cornea to correct vision and improve visual acuity with high precision.
Dermatology
The laser is used for skin resurfacing, removal of scars, pigmentation, and other targeted treatments requiring precise tissue removal.
Cardiology and Research
In experimental procedures, excimer lasers assist in precise tissue ablation for vascular interventions and laboratory studies, contributing to advancements in minimally invasive therapies.
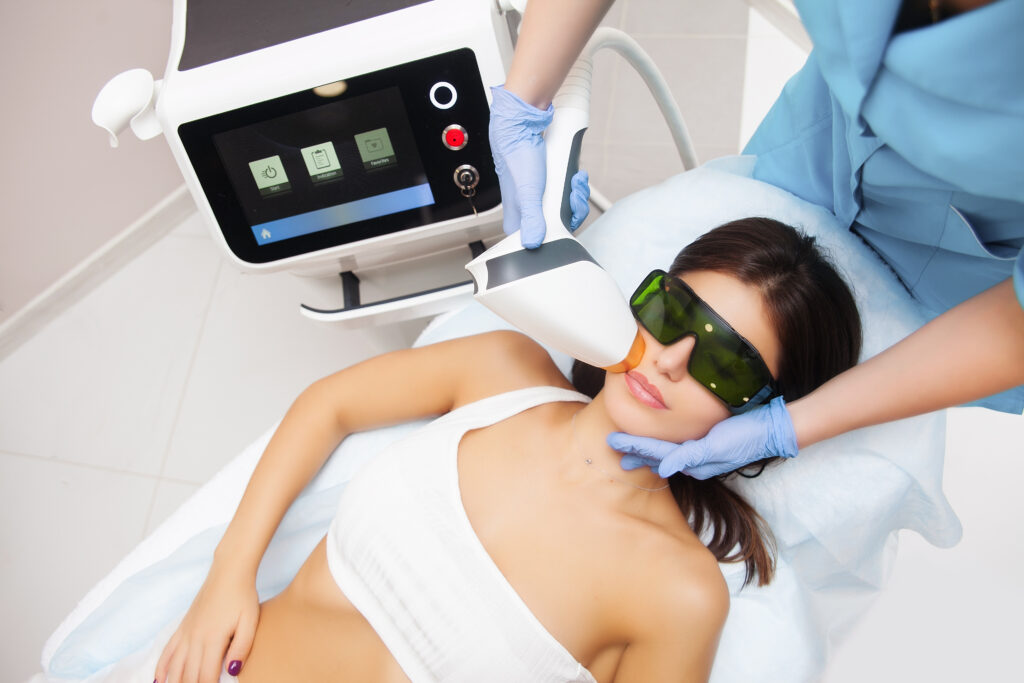
Integration of Advanced Imaging and AI
Modern excimer laser systems often integrate with corneal topography, wavefront analysis, and AI-driven planning software. This ensures precise mapping, personalized treatment patterns, and real-time adjustments during procedures. AI integration enhances safety, improves visual outcomes, and streamlines workflow.
Challenges and Future Perspectives
Excimer laser procedures require specialized equipment, precise calibration, and skilled operators. Limitations include cost, the need for controlled environments, and careful patient selection.
Future developments focus on faster pulse rates, enhanced precision through AI-guided adjustments, integration with robotic-assisted platforms, and expansion into novel therapeutic applications across medicine.
The Broader Impact on Medical Technologies
Excimer lasers exemplify the convergence of precision optics, computer-assisted guidance, and minimally invasive therapy. By enabling controlled, tissue-specific ablation, they improve outcomes, reduce complications, and inspire innovation in surgical and therapeutic procedures across multiple specialties.
Conclusion
Excimer lasers have revolutionized medical procedures by providing precise, safe, and customizable tissue ablation. Their integration into ophthalmology, dermatology, and experimental medicine demonstrates the power of advanced laser technology in modern healthcare. Ongoing innovation continues to enhance precision, expand applications, and improve patient-centered outcomes.